Video Recognition
or Action Recognition, 视频识别或者视频分类任务,针对视频中的连续帧分类(可以是整个视频,亦可以是视频中的某个片段)
DataSet
- UCF101(small, 适用于预训练,人的动作)
- Sports-1M(sports)
- Youtube-8M(多标签分类)
- Kinetics
BenchMark
- Clip & video
It’s from paper published by FAIR (A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition)
For clip, Select X frames as a clip.
For video, Use center crops of 10 clips randomly sampled from the video and average these 10 clips predictions to obtain the final video prediction. - Top1-Acc & Top5-Acc 在预测结果类别的概率向量中,Top-1类别和Top-5类别与Ground Truth Label得到的Accuracy.
- Other(speed or parameters) GFLOPs(Giga Floating-point Operations Per second)
3D-Conv
传统的2D-conv在应用于单帧图片情况下表现良好,但用于多帧视频情况下,会丢失时间关系或者其他序列前后关系(CT或者MRI医学图像)
- 3D-Conv卷积核:
3D-Conv卷积核的维度至少是3,需要区分multiple channels 2d-conv channel和3d-conv之间的区别:
使$C$为channel数,$H$为图片的height,$W$为图片的width, $L$为图片时间维度上的长度,$K$为卷积核在H和W上的尺寸: - 假设$C=1$(这样更方便理解),2d-conv的卷积核大小为$L \times K \times K$, 输出层在L上会收缩为1维;
- 而3d-conv的卷积核大小维$d \times K \times K$, 这里的$d < L$, 输出层在L上将保留顺序信息;
- 若$C \neq 1$, 2d-conv kernel size=$L \times C \times K \times K$, 3d-conv kernel size=$d \times C \times K \times K $;
- L上depth的设置与2d-conv kernel size设置类似,3-3-3, 3-5-5-7-7, 7-7-5-5-3,..etc
In Conclusion: 3d还是2d的核心区别是输出层上的shape是3 dimension还是2 dimension
-
(2+1)D convolutions(introduced by A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition)
原始的3d-conv kernel为$N_{i-1} \times t \times d \times d$, $N_{i}$是第i层的filter number. t是L上的kernel shape(denotes the temporal extent of the filter)
(2+1)D conv, 将3d-conv拆分为一次2d-conv和一次1d-conv,卷积核shape分别为$N_{i-1} \times 1 \times d \times d$和$M_{i} \times t \times 1 \times 1$, $M_{i}=[\frac{td^{2}N_{i-1}N_{i}}{d^{2}N_{i-1}+tN_{i}}]$
Advantages: i, double the number of the nonlinearites in the network due to the additional RELU function; ii, optimization is much easier.
Method
We separate the method into two part, extraction and classification .Introduced by (Unsupervised Learning from Video with Deep Neural Embeddings)
- extraction:
- single-stream:
- Single-frame 2D-CNNs: lack of temporal information.
- 3D-CNNs: or (2+1)D-CNNs
- 2D-3DCNNs:
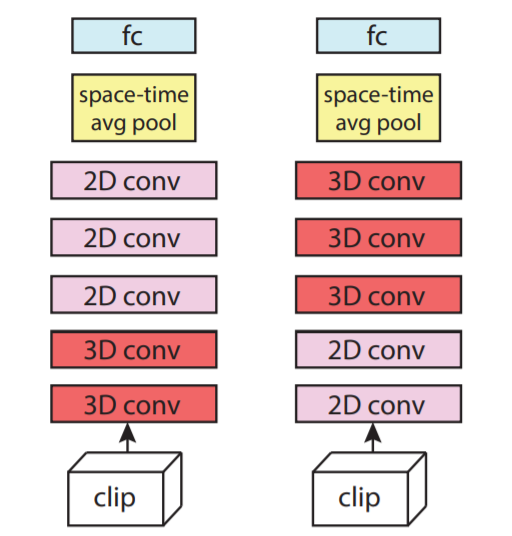
-
two-stream
-
Slow-Fast(introduced by SlowFast Networks for Video Recognition)
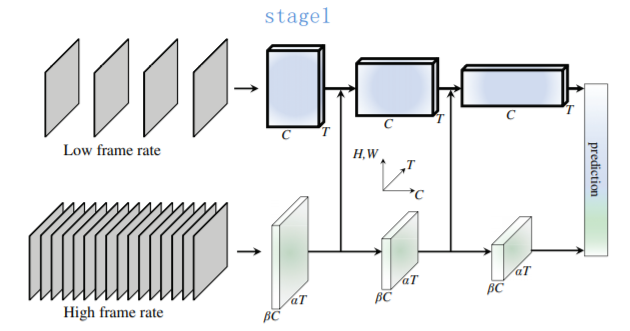
The FAST path: i, high frame rate, up to a typical multiple of $\alpha=8$ than SLOW path; ii, low channel capacity, a typical multiple of $\beta=\frac{1}{8}$ than SLOW path.
-
- single-stream:
-
classification:
-
connection:
- fully-connection after convolutions or pooling,
- lateral connection: In SlowFast, each stage will be connected, And the results of two path will be pooled and concatenated.
-
video-embedding
like word-embedding.
-