Cs131_2 notebook
Resizing, Segmentation and Cluster. More blog and fun, see xiaoxin83121
Chapter5 : Image Resizing
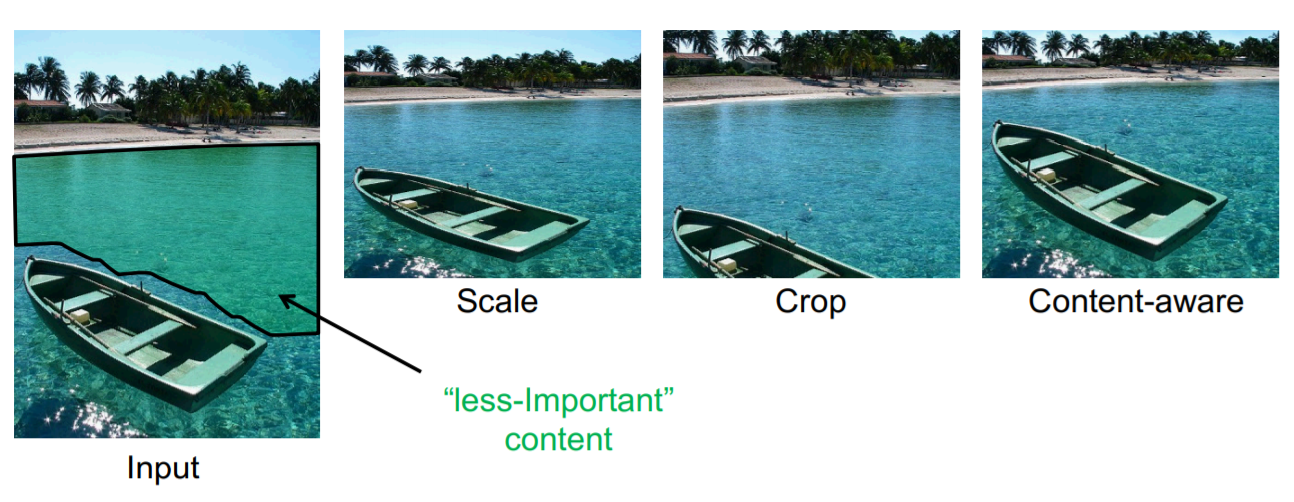
Scale: 对图片进行尺寸上的放缩变换,会对图片内容造成影响;
Crop: 从图片中选出一段区域;
Content-aware: 神奇地去掉不重要的部分;
Energy
Energy is defined as: $E_{1}(I)=|\frac{\part}{\part x}I|+|\frac{\part}{\part y}I|$ , 找到能量最低的点(线、区域),多次剔除即可。如下图的最低能量线(纵向)
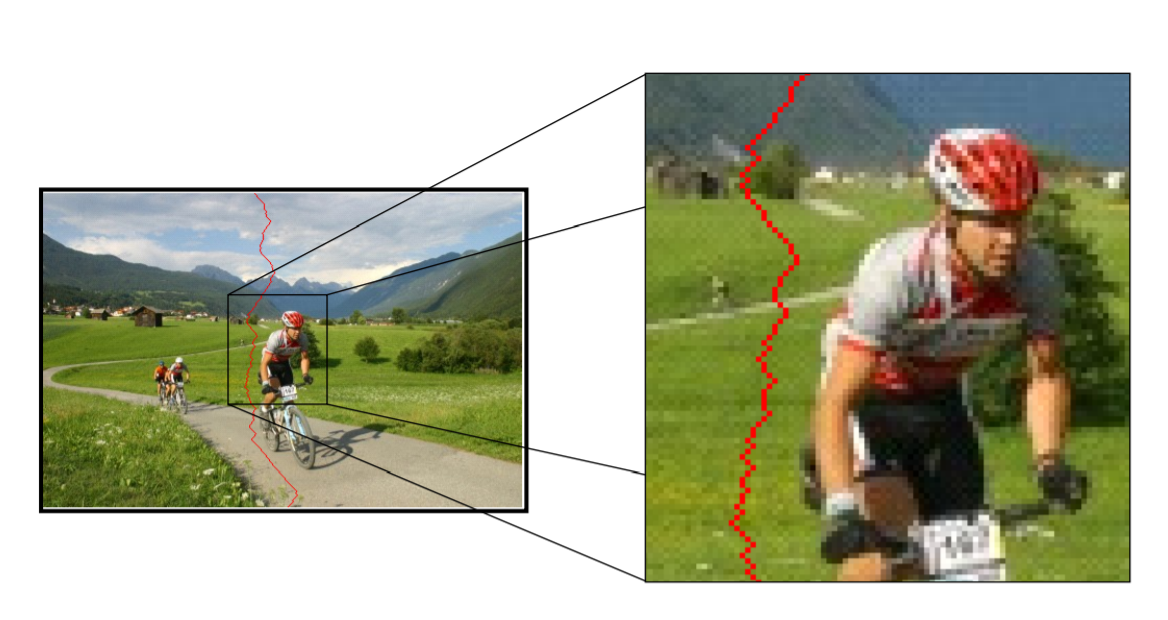
New question! How to find Lowest Energy Line?
The Answer is The Dynamic Programing!!!
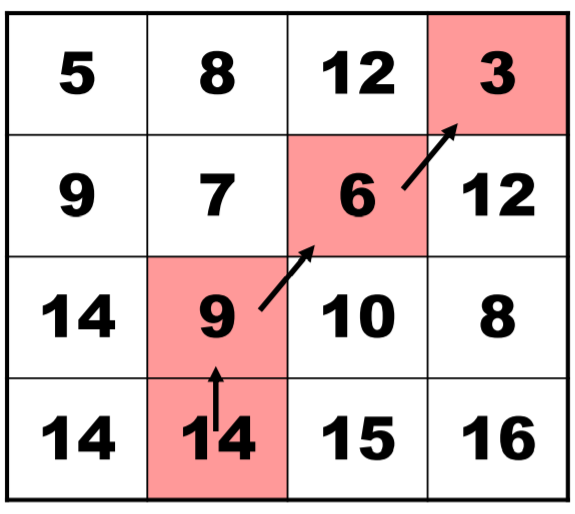
We get the vertical recursion formulation: $M(i,j)=E(i,j)+min(M(i-1,j-1),M(i,j-1),M(i+1,j-1))$
Obviously, it is greedy algorithm. 确定M矩阵后,从最下方开始贪心寻找路线;再剔除掉路线的像素点即可~;持续到满足要求。
code written by python(TODO)
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import cv2
from scipy.ndimage.filters import convolve
import time
def cal_energy_map(img):
filter_h = np.array([[1.0, 2.0, 1.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [-1.0, -2.0, -1.0]])
filter_h = np.stack([filter_h] * 3, axis=2)
filter_v = np.array([[1.0, 0.0, -1.0], [2.0, 0.0, -2.0], [1.0, 0.0, -1.0]])
filter_v = np.stack([filter_v] * 3, axis=2)
img = img.astype('float32')
convolved = np.absolute(convolve(img, filter_v)) + np.absolute(convolve(img, filter_h))
energy_map = convolved.sum(axis=2)
return energy_map
def crop_h(img, scale):
_, w, __ = img.shape
new_w = int(scale * w)
for i in range(w - new_w):
begin_time = time.time()
img = curve(img)
print("Iter-{} cost {}".format(i, time.time()-begin_time))
return img
def crop_v(img, scale):
img = np.rot90(img, 1, (0, 1))
img = crop_h(img, scale)
img = np.rot90(img, -1, (0, 1))
return img
def curve(img):
r, c, _ = img.shape
M, backtrack = minimum_seam(img)
mask = np.ones((r, c), dtype=np.bool)
j = np.argmin(M[-1])
for i in reversed(range(r)):
mask[i, j] = False
j = backtrack[i, j]
mask = np.stack([mask] * 3, axis=2)
img = img[mask].reshape((r, c - 1, 3))
return img
def minimum_seam(img):
r, c, _ = img.shape
energy_map = cal_energy_map(img)
M = energy_map.copy()
backtrack = np.zeros_like(M, dtype=np.int)
for i in range(1, r):
for j in range(0, c):
if j == 0:
idx = np.argmin(M[i-1, j:j + 2])
backtrack[i, j] = idx + j
min_energy = M[i-1, idx + j]
else:
idx = np.argmin(M[i - 1, j - 1:j + 2])
backtrack[i, j] = idx + j - 1
min_energy = M[i - 1, idx + j - 1]
M[i, j] += min_energy
return M, backtrack
if __name__ == "__main__":
image = cv2.imread("./test_seam.jpg")
scale = 0.6
out = crop_v(image, scale)
cv2.imwrite('./test_out.jpg', out)
origin_image: 在嘉峪关没买票拍的

output_image:

Chapter6: Cluster and Segmentation
聚类老熟人了,大概说一下吧就;分割在这里可以狭义的理解为对所有像素进行聚类的结果,早期的医学影像分割同样是像素聚类方法。
聚什么
- 图片的明度(intensity)
- RGB三通道像素值
- ……
怎么聚
核心是点与点之间的距离,欧式距离,余弦距离
- Agglomerative clustering:
- find the a pair of nearest points, merge them as a new ‘point’.
- repeat until there is K ‘point’s.
- k-means
- initialize K cluster centers
- for each point $p$, calculate distance with K centers, add $p$ to points collection of its nearest cluster center
- recompute cluster centers(average, …)
- repeat, until all the points collections stop update
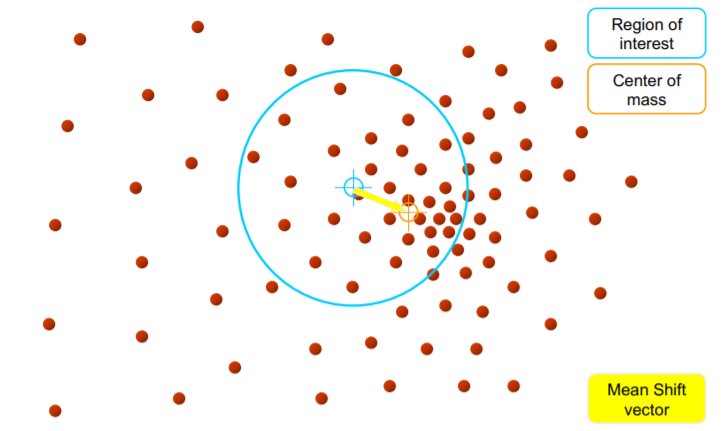
- Mean shift clustering
- initialize window as region of interest
- move window’s center due to weighted average of all points in window
- 所有被同一个窗口扫过的点都将加入同一个类别
- Cons: too many windows and too much computation